
CINEMA : Smart growth of novel thin films of enhanced functional oxides.
Coordinator: Romain BACHELET
INL
Keywords: Smart growth, digital twin, functional perovskite oxides, molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), operando characterizations, thermoelectricity, SrTiO3, p-type oxides, deep learning, convolutional neural networks (CNN)
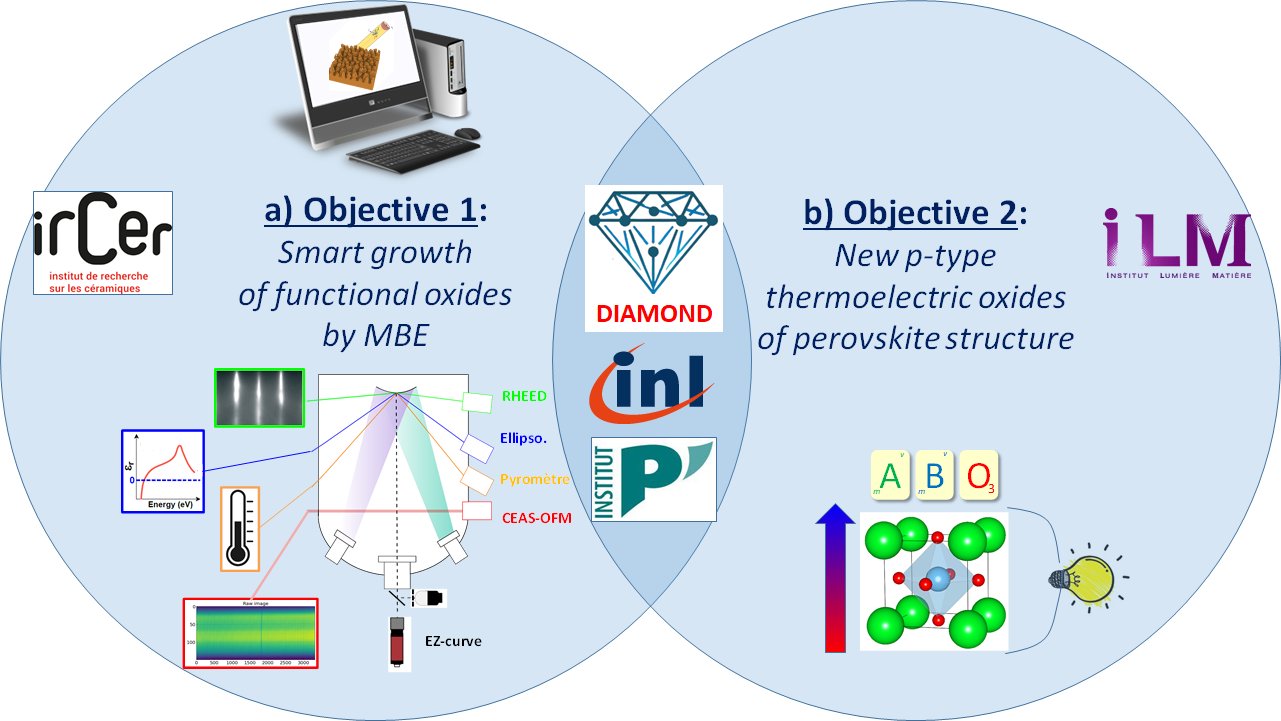
The CINEMA project is an ambitious academic research project aimed at intelligent growth by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) of new thin layers
of improved functional oxides. Regarding the first main objective of smart growth, two approaches will be studied using solid solutions of SrTiO3-based perovskite-structured thermoelectric oxides, which are already well mastered at INL. The first approach is based on operando measurements during growth and deep learning using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. Initially, it will involve coupling numerous in-situ and operando measurements of structural and physical properties during real-time growth (INL).
Secondly, it will include the processing of this data by algorithms using convolutional neural networks (IRCER, INL, DIADEM-DM platform). Thirdly, feedback loops will be set up to control growth by the targeted properties, measured and analyzed in real time. The second approach consists of creating a digital twin of growth through simulations (P’). These simulations will be performed using kinetic Monte Carlo (k-MC) and DFT calculations optimized by AI algorithms (Collab. Univ. Montreal & LAAS). The theoretical results will be compared with experimental results of increasing complexity (binary, ternary, and finally quaternary oxides).
A second joint objective concerns AI prediction and MBE development of new solid solutions for high-performance p-type thermoelectric oxides (PF > 10 μW cm-1 K-2) that are stable and durable (containing non-toxic or low-toxicity and abundant elements). Initially, these predictions will require feeding data into a database and analyzing it (DIADEM-DM platform). Next, the structural stability of these new oxides will be evaluated using DFT calculations (P’). Thirdly, the thermoelectric properties of the most promising new oxides will be estimated using ab initio calculations (ILM). Finally, the most promising solid solutions will be developed in thin layers using AI-assisted MBE, and all of their thermoelectric properties will be measured (INL, ILM).
In addition to the DIADEM-DM platform, this project brings together four recognized and complementary academic partners with all the skills and tools needed to achieve the objectives. This project would accelerate the discovery and mastery of new materials with improved properties in various fields of application, in academic research and industry.